Advantages Make Thin Film Solar Panels Shine
When people think of solar panels, they think of crystalline solar panels. These panels, which are usually blue or black, have a hard glass cover and measure about three by five feet. However, there is an entirely different type of solar panel that you can simply roll out and attach to your roof called thin film solar panels. Thin film market has grown significantly in the past years. In 2002, shipments of thin film was a mere 17 megawatts. With a compound annual growth rate of 80%, shipments of thin film panels approached 3.7 gigawatts, representing 11% of the solar market today.
Low cost no longer the major advantage for thin film
One major advantage of thin film panels has been cost, which is approximately 30% less than crystalline panels. This is mainly due to the module itself and its installation process. According to a Bloomberg report in June 2012, First Solar has brought its price down to $0.75 per watt, 50% less than some crystalline competitors. However, thin film manufacturer's margins have been squeezed a lot as Chinese crystalline manufacturers ramped up production, causing the cost of crystalline modules to plummet. Thin film solar panels represented as much as 18% of the market in 2009, but have retreated significantly since this peak and now represent only 11% of the market. As a result, many thin film solar panel producers have exited the market and low cost is no longer the major advantage for think film modules.
In this learning article, we will discuss the benefits of thin film panels that may persuade you to consider them. We will first describe the technology behind thin film solar modules, because it is the theoretical basis for their advantages. Then we will talk about the three major areas in which thin film panels shine: weak roof support applications, diffused light conversion, and hot weather performance.
The technology behind thin film solar panels
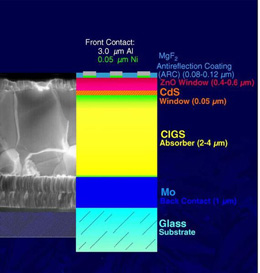
A primer on the technology: Now you may not like to hear the details about the technology, but to understand why there is an important place for thin film modules, you need to know a little about the technology of solar panels and thin film panels in particular.
Solar modules are a connected assembly of many individual electric devices, called solar cells, which convert sunlight to electricity via the photovoltaic (PV) effect. A new technology called a thin film solar cell (TFSC) is a solar cell that is made by depositing one or more thin layers (thin film) of various photovoltaic (PV) materials on a substrate. The PV materials are carefully chosen to absorb a broader range of the solar spectrum that extends beyond visible light. The cell can thus generate electricity from as much of the solar energy as possible. Compared with the dominant crystalline solar modules that have commercial efficiency ratings ranging from 14%-20%, thin film modules are less efficient, converting at 8%-13%. Thin film solar modules can be categorized according to their PV material as one of four distinct technologies:
-
Amorphous silicon (a-Si)
- Cadmium telluride (CdTe)
- Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)
- Dye-sensitized solar cell (DSC)
Related article: The Many Faces of Solar Energy: An Overview of Solar PV Technologies
Working principles on cloudy days: The first doubt customers have when considering solar panels may be: do they work during cloudy days when there is no sunshine? The answer is: Yes, of course!! A natural second question would then be: How do they manage to work on cloudy days?
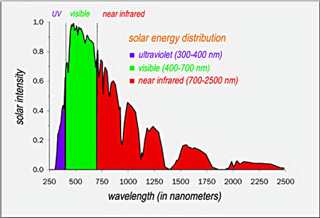
As much as 99.9% of the sunlight spectrum is contained in the ultraviolet, visible light and infrared regions. Each PV material has its own "preference light range," or part of the spectrum where it converts radiation light into electricity with the greatest efficiency. For example, a cell might convert light with a 500-550 nanometer wavelength (green light) or an 800-1000 nanometer wavelength (infrared light) at a much higher efficiency than the rest of the spectrum. To gain an edge over crystalline solar cells, thin-film cells use multiple physical configurations, meaning they include a variety of layers with whose materials have different preference light ranges.
The more sunlight and spectrum range the solar panel absorbs, the higher its efficiency and output. In cloudy weather, most of the direct visible light, what you call sunshine, is blocked by clouds. However, as the sun's rays pass through the atmosphere, small water droplets and other objects scatter visible light, producing diffused light. Therefore, when clouds are not too thick, solar panels still get some visible light because of diffusion. Since infrared light has a longer wavelength than visible light, it can take advantage of diffraction. This effect allows a great amount of infrared light to reach ground. Moreover, there is always some reflected light in the environment. In conclusion, thin film solar panels can produce electricity in cloudy, foggy and rainy weather, producing through the PV effect by absorbing ambient, infrared, and ultraviolet light.
Heat effect in electrical resistance: Many people initially believe that very hot places such as California, Arizona, and Colorado, are ideal for PV panels. In their mind, high temperature means a lot of sunshine which indeed increases the output from solar panels for your homes or businesses. Unfortunately, although sun is the PV panel's best friend, high temperatures are its enemy. Based on semi-conductor material science, heat causes electrical resistance to the flow of electrons in PV layer. As temperature increases, so will the resistance, causing a weaker flow of electrons (lower current). The temperature coefficientis the term used to measure this phenomenon, which is especially prevalent in crystalline materials. In general, it's the light, not the temperature that matters.
Advantages Make Thin Film Panels Shine
Low Rooftop Requirement and More Installation Flexibility: Crystalline solar panel cells are 0.15-0.2 mm thick, whereas thin film cells can be as thin as 0.001 mm and are also much lighter. As opposed to crystalline panels, which are installed on strong rooftops with rugged mounting system tilted at a fixed degree, thin film panels can be rolled out and directly attached to the rooftop on your home or business. This allows them to be installed on any rooftop without racks, even one with weak support. So it's easier and cheaper to install thin film panels. Suppose a home has a 5 kW solar energy system on its roof. The family can save $1,250 since it does not need racking, which is equivalent to $0.25 per watt.

It's not just about money. Flexibility makes thin film solar panels more suitable for sophisticated building-integrated installations, while also satisfying the aesthetic needs of the architect.
Related article: Solar Racking Made Simple: What You Need to Know About Designing Your Solar Energy System
Better performance in hot weather
Solar panels usually get the highest conversion efficiency at 25 degrees C (77 degrees F). However, the temperature of solar module operating in the sun is always higher, especially at the top of a high building. As described in the previous paragraph, crystalline solar panels produce less electricity when the temperature rises above 25 degrees Celsius. But thin film modules are not affected by temperature as much.
Take amorphous silicon(a-Si) modules as an example. According to AmpleSun's research, the temperature coefficient for the solar cell is 0.2%/degree meaning that whenever the temperature increases by 1 degree, the cell's efficiency will decrease by 0.2%. Meanwhile the coefficient of crystalline module is 0.5%/degree. The following table compares the performance of an a-Si rooftop panel to that of a crystalline panel in summer. The temperature is the only variable.
| Condition | Efficiency of solar panel /% | |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature /degree | a-Si thin film | Crystalline |
| 25 (STC) | 10 | 16 |
| 35 | 8 | 11 |
| 45 | 6 | 6 |
| 50 | 5 | 3.5 |
It is commonplace for rooftop solar modules to reach above 45 degrees Celsius in hot areas or during the summer. Therefore, in an environment like Arizona, crystalline and thin film solar panels perform at a similar level. It turns out that an a-Si thin film solar panels will outperform a crystalline panel during the summer even if it has a 40% lower efficiency rating in standard test condition (STC). Therefore, as Bangladesh Trade Economy reports, many mega-watt scale solar energy projects in India, Indonesia, and Bangladesh use thin film modules.
Good fit for cloudy days and weak light condition: Normally, all crystalline panels get good PV performance at STC when solar irradiance is 1000 W/m2. However, they will rarely operate in such ideal conditions. The sunlight spectrum that crystalline cells absorb is from 400nm-1000nm in wavelength, containing mostly visible light (400-800nm: visible; 800nm: infrared). Therefore the efficiency of crystalline solar panels will drop substantially when visible light is blocked by clouds.
Moreover, during very cloudy days or in weak light condition, they can't work. The following table shows the efficiency drop of crystalline solar panels in several typical conditions.
| Condition | Crystalline Efficiency Drop |
|---|---|
| Light San Francisco fog | 8%-15% |
| Heavy San Francisco fog | 15%-20% |
| Cloudy & raining | 20% - 50% |
| Heavy cloudy & raining | 50% - 90% |
Thin film solar panels have a broader spectrum absorption range that includes more infrared and even some ultraviolet light. For example, CIGS takes in sunlight ranging from 400nm-1200nm and CdTe absorbs sunlight from 250nm-1750nm. This feature makes CIGS and CdTe cells convert more sunlight and work for more hours a day than crystalline cells when it's overcast. Furthermore, CIGS and CdTe are less dependent on the intensity and radiation direction of sunshine. In other words, they have better weak light performance, allowing them to generate power in the early morning or late afternoon and on cloudy and rainy days. In conclusion, the efficiency of thin film solar panels will not drop by much in these weak light conditions, making this technology more reliable and powerful.
As the world leader of solar energy, Germany has installed as much solar power generation capacity as the rest of the world combined. Because there are many cloudy days in this country, Germany installs thin film solar modules to generate electricity.
Based on the various advantages of thin film solar panels, many companies are accelerating their production and installation of this technology. For certain features, and given its low cost, thin film solar panels will join crystalline panels as a leading solar technology.
